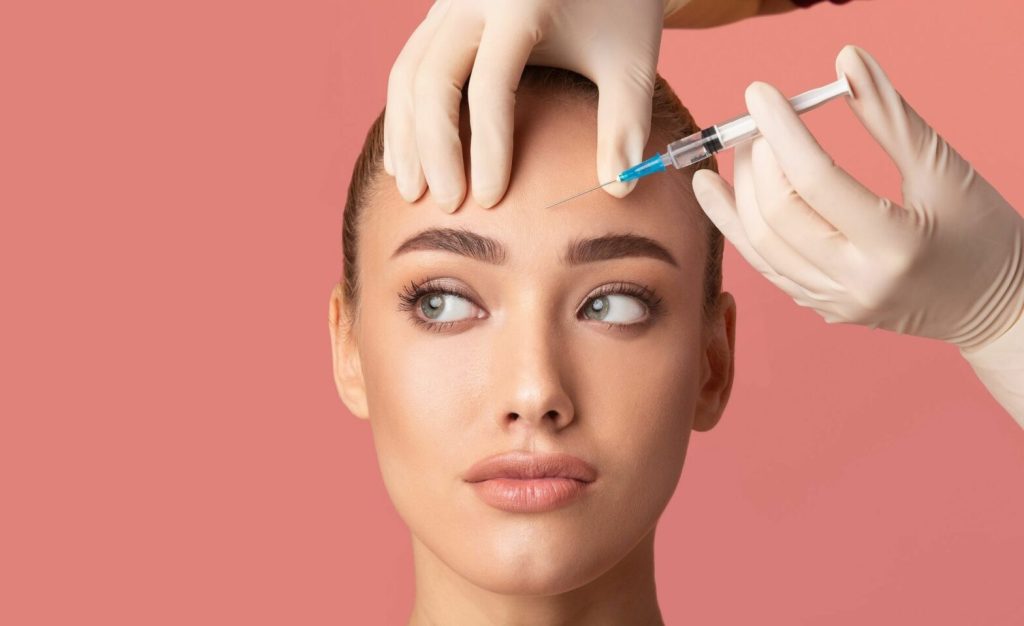
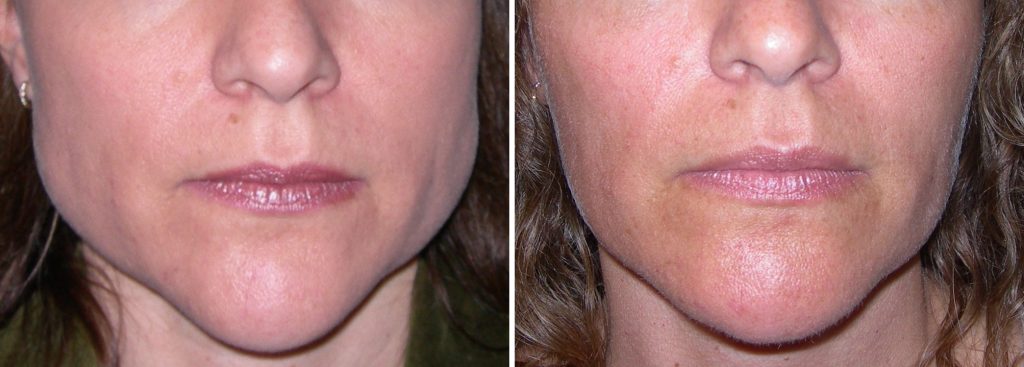
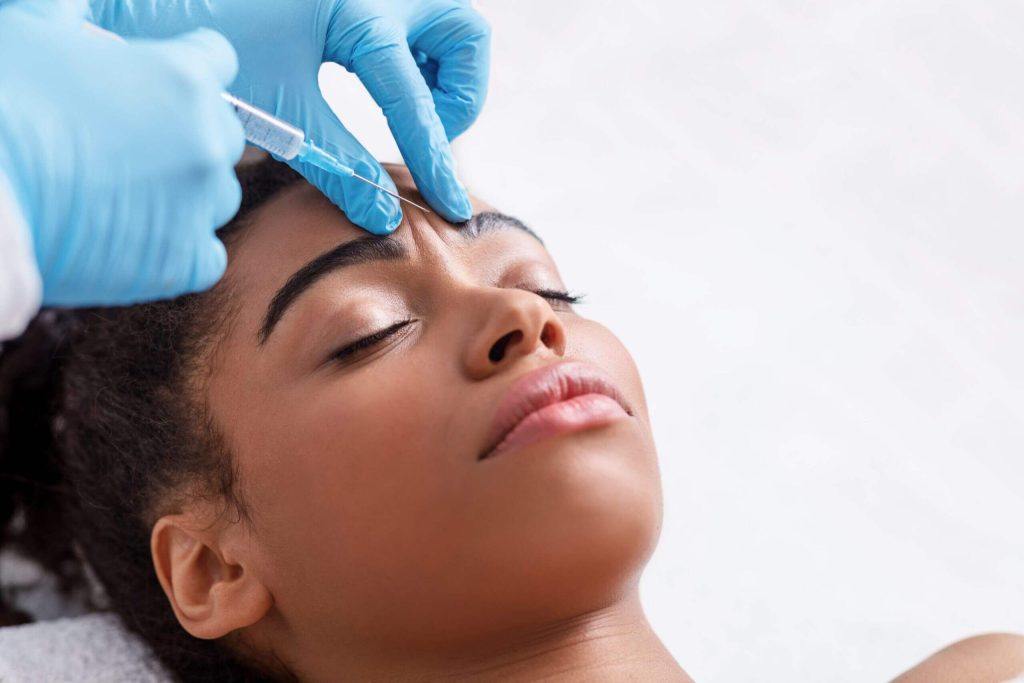
Botulinum neurotoxin, formed by a bacterium called Clostridium botulinum, is the first microbial protein used for therapeutic purposes in humans.
Since the 1970s, Botox has found its use in many medical fields, from the treatment of various medical conditions to aesthetic applications.
What is Botox? How is Botox Applied?
Botox is a drug derived from a toxin produced by a bacterium called Clostridium botulinum. There are 7 alphabetically named neurotoxins (nerve cell poisons) produced by this bacterium, but only types A and B of these toxins have been used clinically in humans.
After Botox injection, the toxin binds to the nerve cell within approximately half an hour. In the ongoing process, Botox causes changes in the chemical properties of the nerve cell to which it binds and stops the nerve from functioning.
The release of the neurotransmitter substance called acetylcholine, which stimulates muscles through nerve cells, is blocked by botulinum toxin and causes temporary relaxation in muscles that cannot be stimulated by the nerve cell in that area.
1
Cervical Dystonia
In cervical dystonia, a painful condition, an abnormal posture position occurs due to involuntary contraction of the neck muscles. Botox applications can be beneficial in relaxing these muscles.
2
Lazy Eye
The eye muscles need to work in a coordinated manner for vision to function fully. In lazy eye, the harmony between these muscles is lost. Botox applications can regulate the harmony of the eye muscles.
3
Muscle Contracture
After changes in muscle cells or nerve cells that stimulate them, the muscles give an abnormal position to the joint in the area where the muscles are located is called contracture.
How is Botox Applied?
The standard dose of toxin used for Botox applications for cosmetic purposes is 20 units. There are different botox brands.
Botulinum toxin is injected directly into the relevant muscle area through the botox needle. In men, higher doses can be used in areas with high regional muscle density. In areas where muscle weakness is already present, lower doses of botox are preferred.
Botox is injected into 3-5 areas by the practitioner. No intervention should be made in that area within the first 2-3 hours after the injection, and the person who receives Botox should stand in an upright position for 3-4 hours during this period. The person who has undergone the application should not strain the muscles in the application area within the first 1-2 days and should rest. Care should be taken, especially in facial applications, as any application that will affect the muscles such as massage in the days following the application may cause the toxin to be released and affect other muscles.
Botox starts to show its effect within the first 4 days following the injection and reaches maximum effectiveness at the end of the 1st month. At the end of 3-4 months after the application, it starts to lose its effect.
Posts
Can Botox Help With Teeth Grinding and Jaw Pain
Have you ever woken up with a sore jaw or dull headache and wondered what happened overnight while you slept peacefully? Many people experience these signs without realizing teeth grinding[…]
Read moreBotox and Aging: How It Fits Into Long-Term Skincare
Botox is often seen as a quick fix for wrinkles, but its role in long-term skincare is far more layered than people assume, and understanding how it works over time[…]
Read moreCombining Botox with Other Aesthetic Treatments
Have you ever noticed how some people achieve a remarkably natural look after cosmetic treatments and wondered how they manage to blend different procedures so seamlessly? Many individuals assume Botox[…]
Read moreBotox and Facial Expressions: What Changes?
Have you ever looked in the mirror after a long day and noticed how every emotion seems written across your face? Many people feel this way because facial expressions form[…]
Read moreBotox Gone Wrong: Common Mistakes and Fixes
You glance in the mirror after a routine session. One brow looks higher than expected. Your smile feels slightly different during photos. Friends say you look tired despite rest. You[…]
Read moreHow Soon After Treatment Will I See Botox Results?
The expectation surrounding a Botulinum Toxin Type A (BTA) treatment, widely known by the brand name Botox, often centers on a desire for immediate cosmetic change. However, the precise timeline[…]
Read moreBotox for Migraine Relief: Does It Really Work Well?
The persistent, often crippling neurological disorder known as chronic migraine presents a significant challenge to both patients and clinicians, particularly when traditional oral prophylactic medications fail to provide adequate relief[…]
Read moreGetting Botox While Pregnant: What You Should Know
The conversation surrounding cosmetic injectables often hits a serious roadblock when the topic turns to pregnancy. The question, “Can you get Botox while pregnant?” is one that aesthetic practitioners face[…]
Read moreBotox and Skincare: What’s the Connection?
The interaction between neuromodulators, commonly referred to by the brand name Botox, and a daily skincare regimen is often misunderstood, viewed simplistically as two separate approaches to cosmetic enhancement. In[…]
Read more